How Does Joint And Several Liability Impact A Personal Injury Case?
 Personal injury accidents like car collisions often involve several parties. Whenever someone is partially to blame for a motor vehicle accident, they could be listed as a defendant and obligated to pay damages if found to be responsible for the plaintiff’s injuries. The rule of joint and several liability applies when there are multiple defendants. New York State’s joint and several liability law allows plaintiffs to hold defendants, individually or collectively, accountable for the total amount of their damages. In these cases, the plaintiff should consider how many defendants were involved, what percentage of fault can be allocated to each party, and each defendant’s automobile insurance policy coverage limits. Many drivers only carry New York’s minimum car insurance liability limits. While this may seem like enough coverage, the damages owed to victims in severe motor vehicle accidents often exceed these amounts.
Personal injury accidents like car collisions often involve several parties. Whenever someone is partially to blame for a motor vehicle accident, they could be listed as a defendant and obligated to pay damages if found to be responsible for the plaintiff’s injuries. The rule of joint and several liability applies when there are multiple defendants. New York State’s joint and several liability law allows plaintiffs to hold defendants, individually or collectively, accountable for the total amount of their damages. In these cases, the plaintiff should consider how many defendants were involved, what percentage of fault can be allocated to each party, and each defendant’s automobile insurance policy coverage limits. Many drivers only carry New York’s minimum car insurance liability limits. While this may seem like enough coverage, the damages owed to victims in severe motor vehicle accidents often exceed these amounts.
Joint Liability Vs. Joint And Several Liability
Joint and joint and several liability legal principles allow victims to hold multiple defendants accountable for their actions. Joint liability differs from joint and several liability in that, in the first instance, the responsibility is spread equally among all of the defendants. In the latter, the responsibility shifts depending on the determined percentage of each defendant’s liability. A judge or a jury typically makes this determination. In New York State, defendants generally are held joint and severally responsible.
 Buffalo Personal Injury Lawyer News
Buffalo Personal Injury Lawyer News
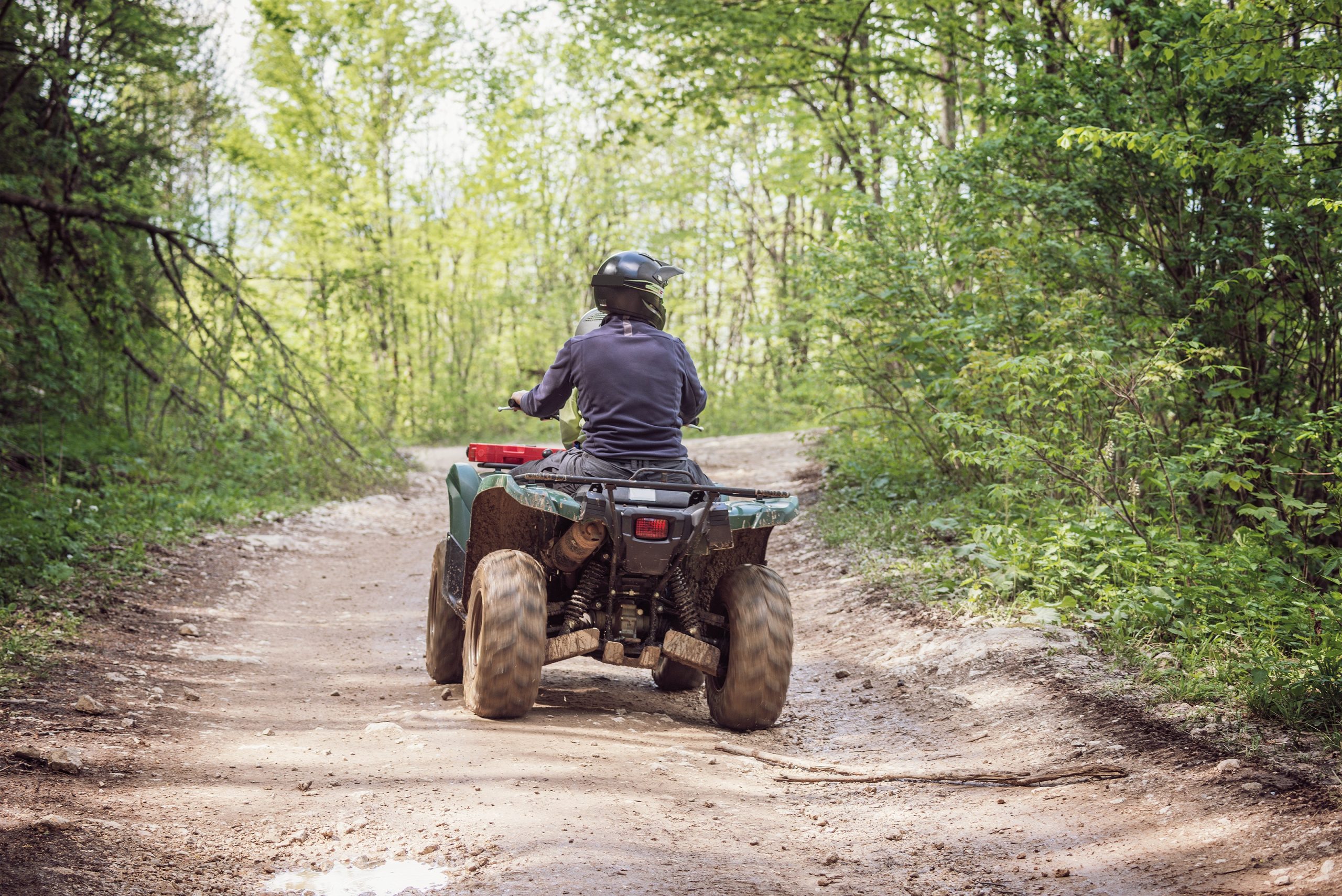

 New York State is home to some of the best All-Terrain Vehicle (ATV) parks and trails in the United States. Whether you are considering purchasing a four-wheeler or already own one, it is imperative to familiarize yourself with some of the relevant laws and safety precautions. Below, the Dietrich Law Firm P.C.’s battle-tested ATV accident injury lawyers have gathered some vital information.
New York State is home to some of the best All-Terrain Vehicle (ATV) parks and trails in the United States. Whether you are considering purchasing a four-wheeler or already own one, it is imperative to familiarize yourself with some of the relevant laws and safety precautions. Below, the Dietrich Law Firm P.C.’s battle-tested ATV accident injury lawyers have gathered some vital information.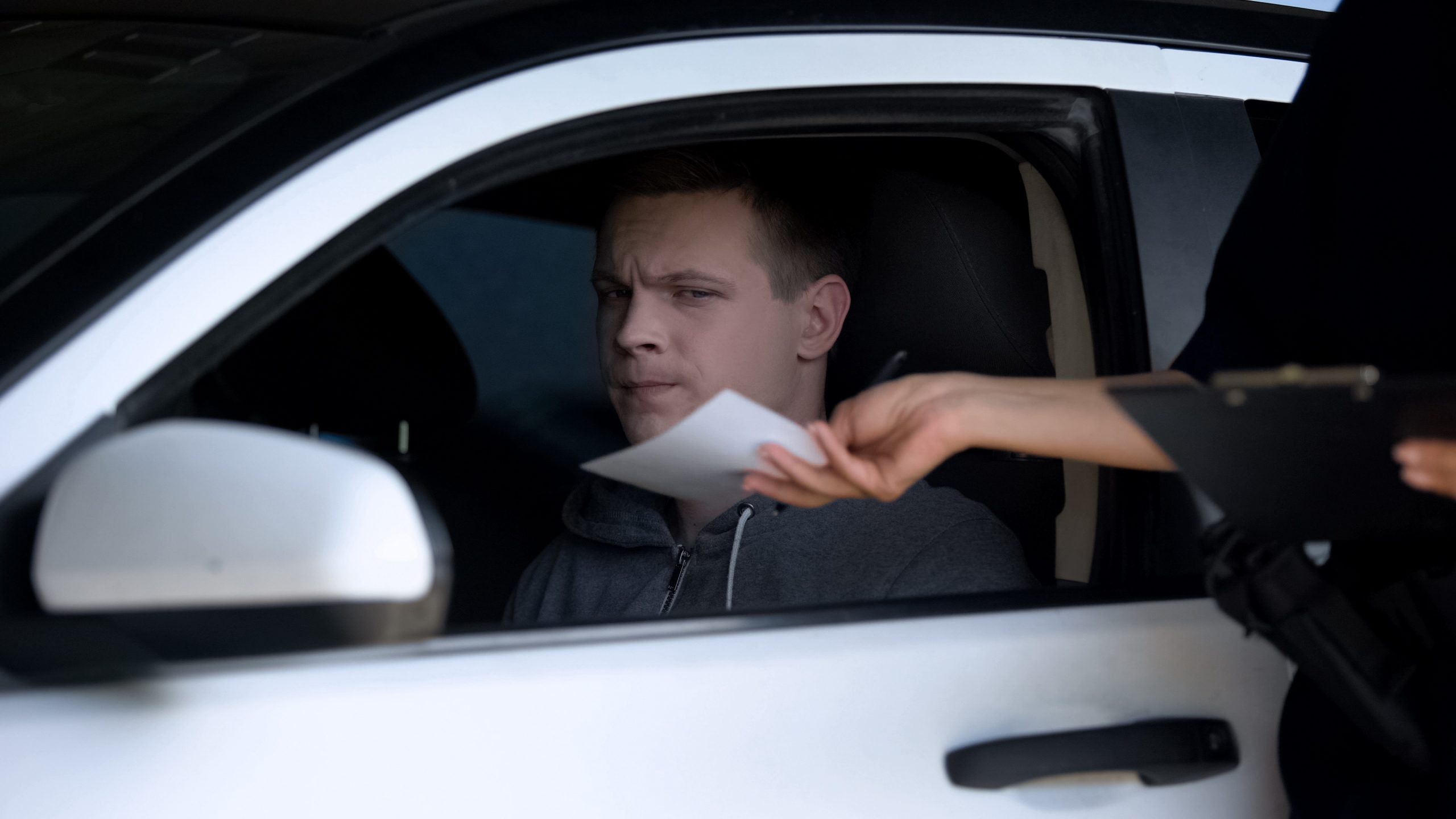 Upon arriving at the scene of a car crash, the police will investigate to determine which driver is at fault. During this time, the officers typically interview the drivers involved and bystanders who witnessed the accident. Should the police conclude that a driver violated the New York State Vehicle and Traffic Law, they will issue a traffic ticket, also known as a citation. Consequently, the driver who received the ticket must go to traffic court. Suppose the other motorist suffered any damage, such as injuries, lost wages, or property damage. In that case, they might seek monetary compensation through a personal injury claim. Many car accident victims wonder whether the outcome of traffic court will impact their case against the ticketed driver.
Upon arriving at the scene of a car crash, the police will investigate to determine which driver is at fault. During this time, the officers typically interview the drivers involved and bystanders who witnessed the accident. Should the police conclude that a driver violated the New York State Vehicle and Traffic Law, they will issue a traffic ticket, also known as a citation. Consequently, the driver who received the ticket must go to traffic court. Suppose the other motorist suffered any damage, such as injuries, lost wages, or property damage. In that case, they might seek monetary compensation through a personal injury claim. Many car accident victims wonder whether the outcome of traffic court will impact their case against the ticketed driver.  Suppose that you, or a family member, has been severely injured in an accident caused by someone else’s negligence or even recklessness. In such an unfortunate case, it is only natural to want the finest personal injury lawyer you can find. While many attorneys may be able to provide you with competent legal advice, certain traits distinguish good lawyers from the best.
Suppose that you, or a family member, has been severely injured in an accident caused by someone else’s negligence or even recklessness. In such an unfortunate case, it is only natural to want the finest personal injury lawyer you can find. While many attorneys may be able to provide you with competent legal advice, certain traits distinguish good lawyers from the best.  Although the last thing anyone wants is to be the victim of an accident, mishaps are part of life. To better safeguard you and your loved ones, it is imperative to be aware of the most prevalent types of accidents. Below, the Dietrich Law Firm P.C.’s team of personal injury lawyers has listed the most frequently occurring accidents along with crucial tips to avoid them:
Although the last thing anyone wants is to be the victim of an accident, mishaps are part of life. To better safeguard you and your loved ones, it is imperative to be aware of the most prevalent types of accidents. Below, the Dietrich Law Firm P.C.’s team of personal injury lawyers has listed the most frequently occurring accidents along with crucial tips to avoid them:  The vast majority of all personal injury claims are resolved outside of courtrooms through settlements. A settlement agreement is a legally binding contract between the victim and the defendant whom they filed the lawsuit against. The terms of a settlement are negotiated back and forth until an agreement can be reached. Once negotiations have concluded, and a settlement amount is agreed upon, you will have to review and sign a release of liability form before your check is processed.
The vast majority of all personal injury claims are resolved outside of courtrooms through settlements. A settlement agreement is a legally binding contract between the victim and the defendant whom they filed the lawsuit against. The terms of a settlement are negotiated back and forth until an agreement can be reached. Once negotiations have concluded, and a settlement amount is agreed upon, you will have to review and sign a release of liability form before your check is processed.  Most personal injury lawsuits begin with a case evaluation and consultation. Often, it is the first time you will discuss your claim with a lawyer face-to-face. At an initial consultation, one of our elite lawyers will assess the merits of your potential case. The attorney will also determine if your specific needs match our legal services. Initial consultations are a beneficial process for everyone involved. It allows the lawyer to understand how the accident happened, the scope and severity of your injuries, the medical treatment involved, your future prognosis, and other damages. You must be adequately prepared for your complimentary consultation. Our attorneys request that potential clients speak openly and honestly so that we can get all the required information.
Most personal injury lawsuits begin with a case evaluation and consultation. Often, it is the first time you will discuss your claim with a lawyer face-to-face. At an initial consultation, one of our elite lawyers will assess the merits of your potential case. The attorney will also determine if your specific needs match our legal services. Initial consultations are a beneficial process for everyone involved. It allows the lawyer to understand how the accident happened, the scope and severity of your injuries, the medical treatment involved, your future prognosis, and other damages. You must be adequately prepared for your complimentary consultation. Our attorneys request that potential clients speak openly and honestly so that we can get all the required information.  Suppose that you, or a family member, have been injured in an accident caused by another person’s negligence or recklessness. You may be able to file a personal injury lawsuit. Pursuing a case against the responsible party could be your only means to recover compensation. However, you only have a limited time to file your claim. The deadline is known as the statute of limitations (SOL). The statute of limitations, like a countdown, can significantly impact when or even if you can pursue your case. Regardless of the strength of your claim, when the statute of limitations runs out, your case will be considered time-barred. Meaning the defendant can assert that the statute of limitations has run out and ask the court to dismiss the lawsuit on that basis alone.
Suppose that you, or a family member, have been injured in an accident caused by another person’s negligence or recklessness. You may be able to file a personal injury lawsuit. Pursuing a case against the responsible party could be your only means to recover compensation. However, you only have a limited time to file your claim. The deadline is known as the statute of limitations (SOL). The statute of limitations, like a countdown, can significantly impact when or even if you can pursue your case. Regardless of the strength of your claim, when the statute of limitations runs out, your case will be considered time-barred. Meaning the defendant can assert that the statute of limitations has run out and ask the court to dismiss the lawsuit on that basis alone. Driving is the most dangerous activity the average American performs multiple times daily. When most people get behind the wheel, the thought of getting into a car accident never even crosses their minds. Drivers are more focused on reaching their destinations quickly. However, motorists are exposed to varying risks during their commutes depending on the time of day, day of the week, and time of the year. While the last thing any driver wants is to be seriously injured in a crash, car accidents are a part of driving.
Driving is the most dangerous activity the average American performs multiple times daily. When most people get behind the wheel, the thought of getting into a car accident never even crosses their minds. Drivers are more focused on reaching their destinations quickly. However, motorists are exposed to varying risks during their commutes depending on the time of day, day of the week, and time of the year. While the last thing any driver wants is to be seriously injured in a crash, car accidents are a part of driving. The human spine comprises 33 vertebrae, each separated by a spongy member referred to as a disc. Each spinal disc contains a jellylike nucleus encased in a rubbery exterior called an annulus. These discs act as shock absorbers and cushions for the spine. Back injuries are often excruciating and can make it difficult for victims to move. One of the most common back injuries is a slipped disc, also called a bulging or herniated disc. As many as 2 percent of adults throughout the United States suffer from slipped discs each year. This type of injury occurs when a portion of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the exterior. While any spine segment can suffer a slipped disc, most occur in the lower back. When left untreated, herniated discs can potentially cause permanent and life-altering complications.
The human spine comprises 33 vertebrae, each separated by a spongy member referred to as a disc. Each spinal disc contains a jellylike nucleus encased in a rubbery exterior called an annulus. These discs act as shock absorbers and cushions for the spine. Back injuries are often excruciating and can make it difficult for victims to move. One of the most common back injuries is a slipped disc, also called a bulging or herniated disc. As many as 2 percent of adults throughout the United States suffer from slipped discs each year. This type of injury occurs when a portion of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the exterior. While any spine segment can suffer a slipped disc, most occur in the lower back. When left untreated, herniated discs can potentially cause permanent and life-altering complications.